ProCrea Introduces Two Approaches to Inset Customization
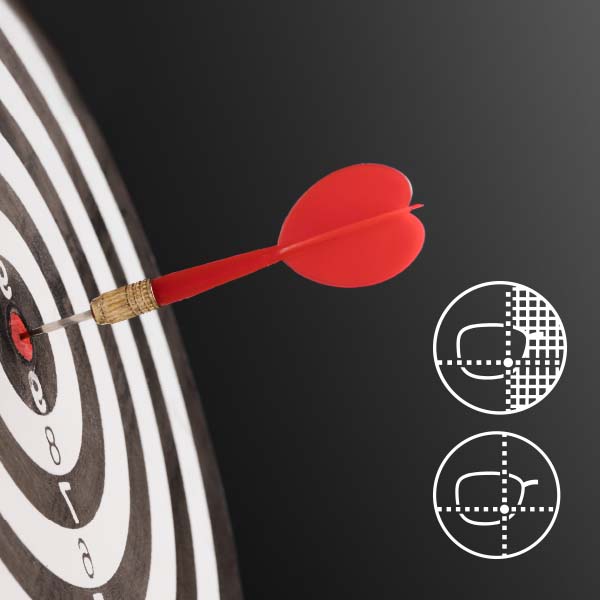

At ProCrea, we know that inset—the horizontal shift of the near vision zone—is essential for wearer comfort in progressive lenses. That’s why we offer two distinct calculation methods.
Our advanced Smart Inset technology leads the way by incorporating a full set of Position-of-Wear parameters—such as interpupillary distance, fitting height, and frame angles—to craft lenses perfectly aligned with each wearer’s unique visual behavior and anatomy. This delivers superior comfort, clearer vision, and easier adaptation.
For straightforward and efficient production, Auto Inset provides a reliable solution based solely on addition power, suitable for standard prescriptions and mass manufacturing.
With ProCrea, you have the flexibility to choose the inset customization that best fits your customers’ needs—ensuring optimal comfort and visual performance.
Smart Inset
Advanced Customization for Optimal Visual Comfort

Smart Inset is ProCrea’s cutting-edge technology for the precise customization of the inset value in progressive lens design. Unlike traditional methods that rely solely on addition power and generic averages, Smart Inset integrates a comprehensive set of Position-of-Wear (PoW) parameters to tailor the near vision zone precisely to each wearer’s unique anatomy and visual behavior.
Key parameters analyzed include:
- Interpupillary Distance (IPD)
- Fitting Height
- Pantoscopic Tilt
- Back Vertex Distance
- Frame Wrap Angle
- Near Working Distance
This holistic approach ensures that the inset—the horizontal shift of the near vision zone—is perfectly aligned with the wearer’s actual eye convergence path, reflecting where the eyes naturally focus during near tasks such as reading, computer use, or smartphone interaction.
Why Customized Inset Matters
The inset plays a vital role in binocular vision balance and ergonomic eye movement. An inaccurately positioned near zone can cause the wearer to compensate with unnatural head or eye movements, resulting in:
- Visual fatigue and strain
- Discomfort during prolonged near work
- Reduced clarity and image stability
- Increased adaptation times and wearer dissatisfaction
By contrast, a customized inset based on full PoW data improves:
- Visual comfort, by reducing eye and head movement required to access near vision zones
- Binocular alignment, enhancing depth perception and image stability
- Adaptation speed, allowing wearers to adjust quickly and confidently to their lenses
- Overall wearer satisfaction and sustained usage
Delivering Personalized Vision—Not One-Size-Fits-All
With Smart Inset, ProCrea empowers labs and lens manufacturers to create progressive lenses that adapt to the wearer’s natural visual behavior, rather than forcing the wearer to adapt to the lens design. This leads to an intuitive, ergonomic experience with smoother transitions, expanded functional zones, and enhanced clarity—ultimately elevating the standard of care and wearer quality of life.
Auto Inset
The Standard Approach to Near Zone Positioning
Auto Inset represents the conventional method used in progressive lens design to determine the inset value—the horizontal shift of the near vision zone relative to the distance optical center.
This method is based solely on the addition power, using average wearer data to estimate the amount of convergence needed for near tasks. While effective for general use, Auto Inset does not take into account individual anatomical or fitting parameters, such as interpupillary distance, frame shape, or head posture.
As a result, the near zone is positioned according to standardized assumptions rather than wearer-specific needs. This approach provides a reliable and efficient solution for mass production of progressive lenses and is well suited for entry-level designs, where full personalization may not be required.
Although less precise than advanced methods like Smart Inset, Auto Inset remains a fundamental and widely adopted technique in the lens industry—ensuring good binocular alignment for the majority of wearers under typical visual conditions.